

AWS COE Challenges
Create a simple FAQ micro-service. The micro-service will return a JSON object containing a random question and answer pair using an Amazon API Gateway endpoint that invokes an AWS Lambda function. Here is the architecture pattern for the micro-service:
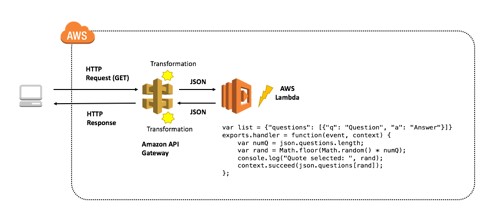
By the end of this exercise, you will be able to:
Estimated Duration: 55 minutes.
Execution
AWS Console
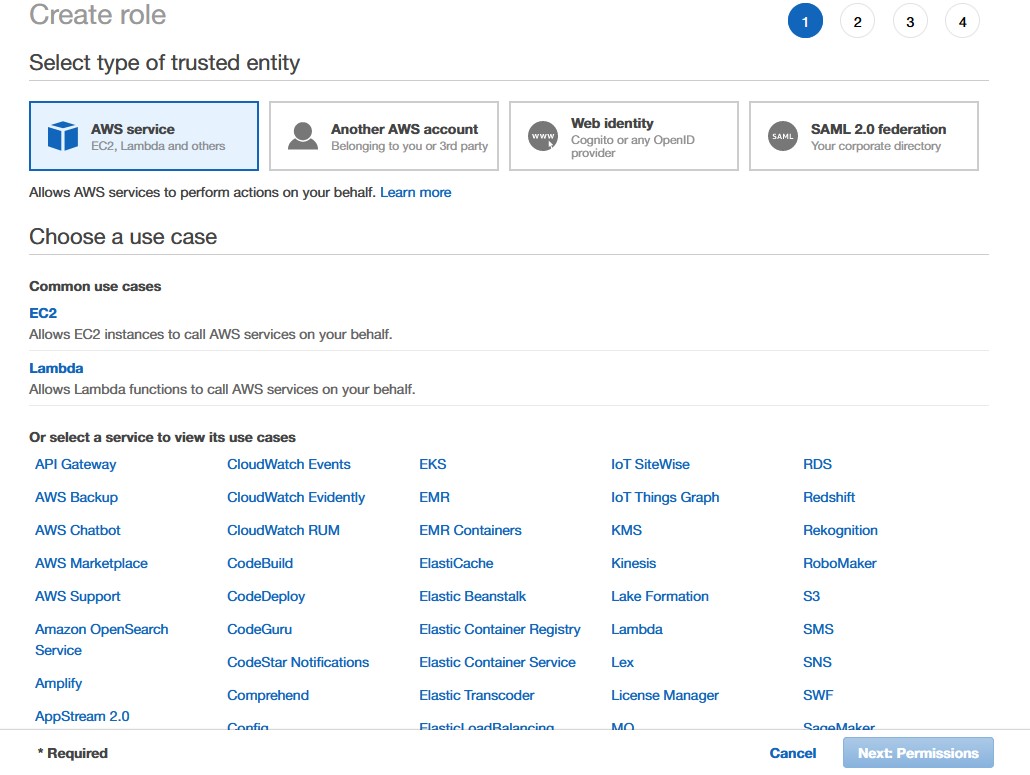
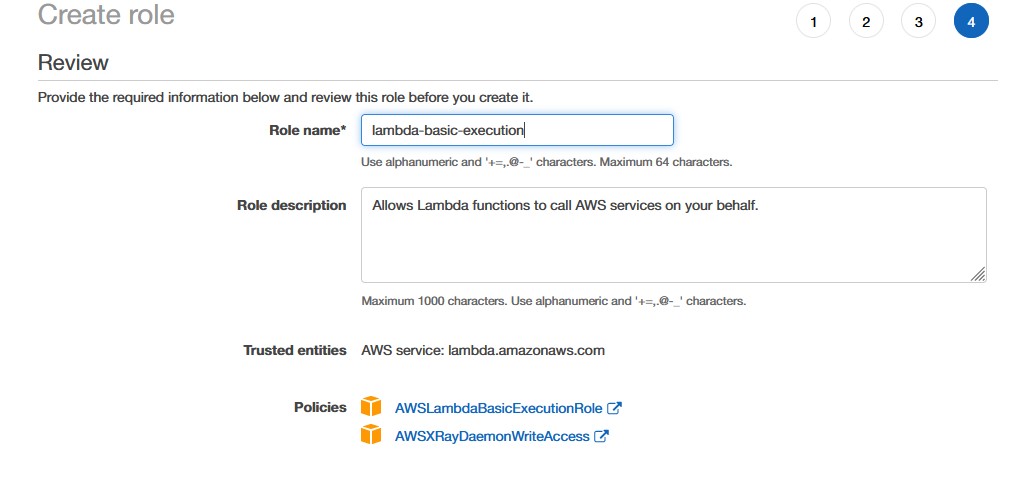
1. Open the Roles page in the IAM console 2. Choose Create role.

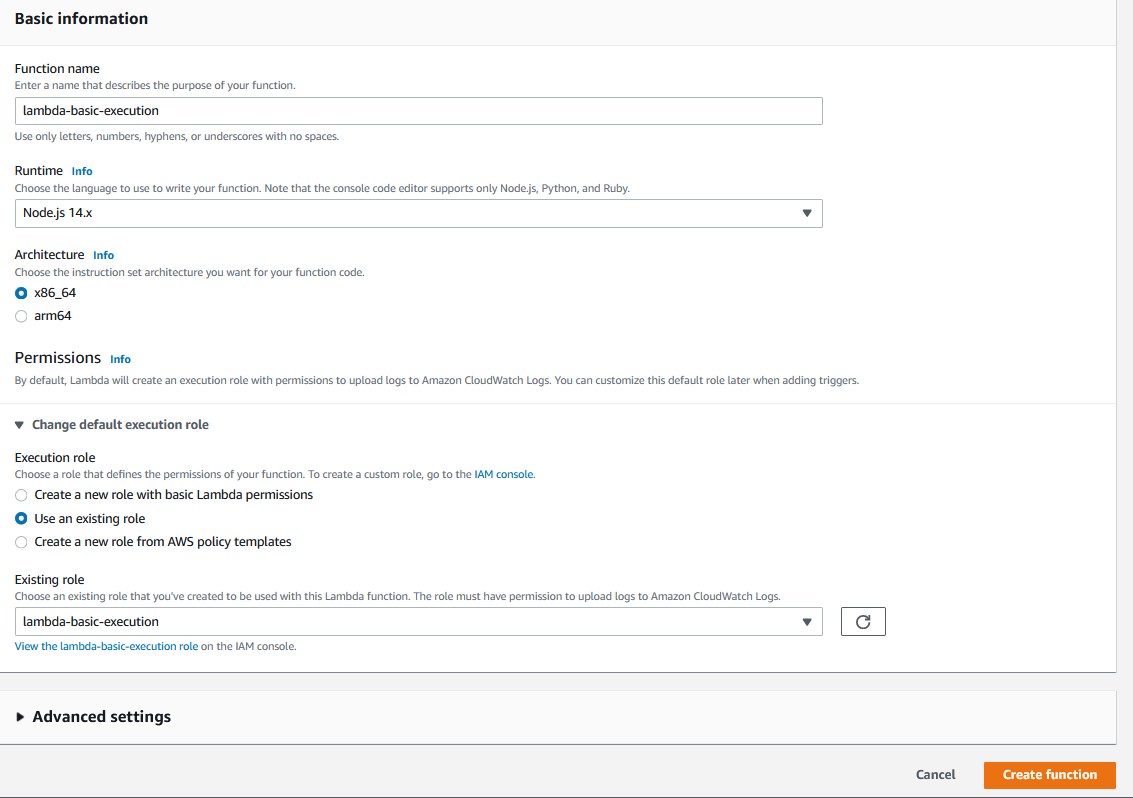
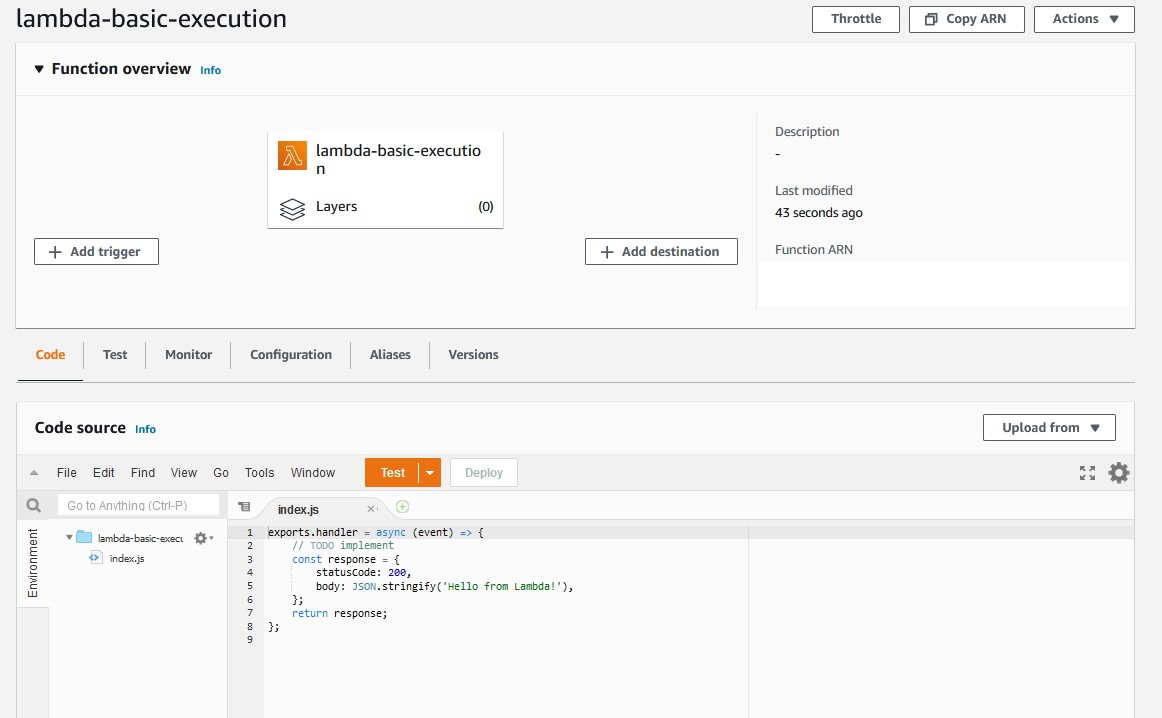
A page will be displayed with your function configuration.
var json = {
"service": "lambda",
"reference": "https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/faqs/",
"questions": [{
"q": "What is AWS Lambda?",
"a": "AWS Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You pay only for the compute time you consume - there is no charge when your code is not running. With Lambda, you can run code for virtually any type of application or backend service - all with zero administration. Just upload your code and Lambda takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability. You can set up your code to automatically trigger from other AWS services or call it directly from any web or mobile app."
},{
"q":"What events can trigger an AWS Lambda function?",
"a":"You can use AWS Lambda to respond to table updates in Amazon DynamoDB, modifications to objects in Amazon S3 buckets, logs arriving in Amazon CloudWatch logs, incoming emails to Amazon Simple Email Service, notifications sent from Amazon SNS, messages arriving in an Amazon Kinesis stream, client data synchronization events in Amazon Cognito, and custom events from mobile applications, web applications, or other web services. You can also invoke a Lambda function on a defined schedule using the AWS Lambda console."
},{
"q":"When should I use AWS Lambda versus Amazon EC2?",
"a":"Amazon Web Services offers a set of compute services to meet a range of needs. Amazon EC2 offers flexibility, with a wide range of instance types and the option to customize the operating system, network and security settings, and the
|
entire software stack, allowing you to easily move existing applications to the cloud. With Amazon EC2 you are responsible for provisioning capacity, monitoring fleet health and performance, and designing for fault tolerance and scalability. AWS Elastic Beanstalk offers an easy-to-use service for deploying and scaling web applications in which you retain ownership and full control over the underlying EC2 instances. Amazon Elastic Container Service is a scalable management service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run distributed applications on a managed cluster of Amazon EC2 instances. AWS Lambda makes it easy to execute code in response to events, such as changes to Amazon S3 buckets, updates to an Amazon DynamoDB table, or custom events generated by your applications or devices. With Lambda you do not have to provision your own instances; Lambda performs all the operational and administrative activities on your behalf, including capacity provisioning, monitoring fleet health, applying security patches to the underlying compute resources, deploying your code, running a web service front end, and monitoring and logging your code. AWS Lambda provides easy scaling and high availability to your code without additional effort on your part." },{ "q":"What kind of code can run on AWS Lambda?", "a":"AWS Lambda offers an easy way to accomplish many activities in the cloud. For example, you can use AWS Lambda to build mobile back-ends that retrieve and transform data from Amazon DynamoDB, handlers that compress or transform objects as they are uploaded to Amazon S3, auditing and reporting of API calls made to any Amazon Web Service, and server-less processing of streaming data using Amazon Kinesis." },{ "q":"What languages does AWS Lambda support?", "a":"AWS Lambda supports code written in Node.js (JavaScript), Python, and Java (Java 8 compatible). Your code can include existing libraries, even native ones. Lambda functions can easily launch processes using languages supported by Amazon Linux, including Bash, Go, and Ruby. Please read our documentation on using Node.js, Python and Java." },{ "q":"Can I access the infrastructure that AWS Lambda runs on?", "a":"No. AWS Lambda operates the compute infrastructure on your behalf, allowing it to perform health checks, apply security patches, and do other routine maintenance." },{ "q":"How does AWS Lambda isolate my code?", "a":"Each AWS Lambda function runs in its own isolated environment, with its own resources and file system view. AWS Lambda uses the same techniques as Amazon EC2 to provide security and separation at the infrastructure and execution levels." },{ "q":"How does AWS Lambda secure my code?", "a":"AWS Lambda stores code in Amazon S3 and encrypts it at rest. AWS Lambda performs additional integrity checks while your code is in use." },{ "q":"What is an AWS Lambda function?", "a":"The code you run on AWS Lambda is uploaded as a Lambda function. Each function has associated configuration information, such as its name, description, entry point, and resource requirements. The code must be written in a stateless style i.e. it should assume there is no affinity to the underlying compute infrastructure. Local file system access, child processes, and similar artifacts may not extend beyond the lifetime of the request, and any persistent state should be stored in Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, or another Internet-available storage service. Lambda functions can include libraries, even native ones." |
|
},{ "q":"Will AWS Lambda reuse function instances?", "a":"To improve performance, AWS Lambda may choose to retain an instance of your function and reuse it to serve a subsequent request, rather than creating a new copy. Your code should not assume that this will always happen." },{ "q":"What if I need scratch space on disk for my AWS Lambda function?", "a":"Each Lambda function receives 500MB of non-persistent disk space in its own /tmp directory." },{ "q":"Why must AWS Lambda functions be stateless?", "a":"Keeping functions stateless enables AWS Lambda to rapidly launch as many copies of the function as needed to scale to the rate of incoming events. While AWS Lambda's programming model is stateless, your code can access stateful data by calling other web services, such as Amazon S3 or Amazon DynamoDB." },{ "q":"Can I use threads and processes in my AWS Lambda function code?", "a":"Yes. AWS Lambda allows you to use normal language and operating system features, such as creating additional threads and processes. Resources allocated to the Lambda function, including memory, execution time, disk, and network use, must be shared among all the threads/processes it uses. You can launch processes using any language supported by Amazon Linux." },{ "q":"What restrictions apply to AWS Lambda function code?", "a":"Lambda attempts to impose few restrictions on normal language and operating system activities, but there are a few activities that are disabled: Inbound network connections are managed by AWS Lambda, only TCP/IP sockets are supported, and ptrace (debugging) system calls are restricted. TCP port 25 traffic is also restricted as an anti-spam measure." },{ "q":"How do I create an AWS Lambda function using the Lambda console?", "a":"You can author the code for your function using the inline editor in the AWS Lambda console. You can also package the code (and any dependent libraries) as a ZIP and upload it using the AWS Lambda console from your local environment or specify an Amazon S3 location where the ZIP file is located. Uploads must be no larger than 50MB (compressed). You can use the AWS Eclipse plugin to author and deploy Lambda functions in Java and Node.js. If you are using Node.js, you can author the code for your function using the inline editor in the AWS Lambda console. Go to the console to get started." },{ "q":"How do I create an AWS Lambda function using the Lambda CLI?", "a":"You can package the code (and any dependent libraries) as a ZIP and upload it using the AWS CLI from your local environment, or specify an Amazon S3 location where the ZIP file is located. Uploads must be no larger than 50MB (compressed). Visit the Lambda Getting Started guide to get started." },{ "q":"Which versions of Python are supported?", "a":"Lambda provides a Python 2.7-compatible runtime to execute your Lambda functions. Lambda will include the latest AWS SDK for Python (boto3) by default." },{ "q":"How do I compile my AWS Lambda function Java code?", "a":"You can use standard tools like Maven or Gradle to compile your Lambda function. Your build process should mimic the same build process you would use to compile any Java code that depends on the AWS SDK. Run your Java compiler tool on |
|
your source files and include the AWS SDK 1.9 or later with transitive dependencies on your classpath. For more details, see our documentation." },{ "q":"What is the JVM environment Lambda uses for execution of my function?", "a":"Lambda provides the Amazon Linux build of openjdk 1.8." } ] } exports.handler = function(event, context) { var rand = Math.floor(Math.random() * json.questions.length); console.log("Quote selected: ", rand);
var response = { body: JSON.stringify(json.questions[rand]) }; console.log(response); context.succeed(response); }; |
Examine the code. It is performing the following steps:
AWS Lambda functions can be triggered automatically by activities such as data being received by Amazon Kinesis or data being updated in an Amazon DynamoDB database. For this challenge, you will trigger the Lambda function whenever a call is made to API Gateway.
An API endpoint refers to a host name of the API. The API endpoint can be edge-optimized or regional, depending on where most of your API traffic originates from. You choose a specific endpoint type when creating an API.
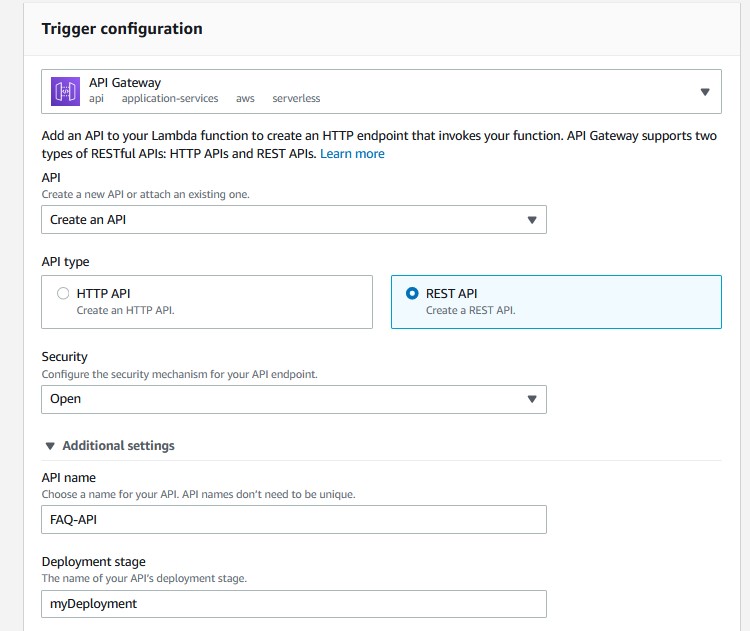
You have successfully created the Lambda function. This has also created a default API Gateway that will trigger the Lambda function.
You will be presented with the FAQ Lambda function page.
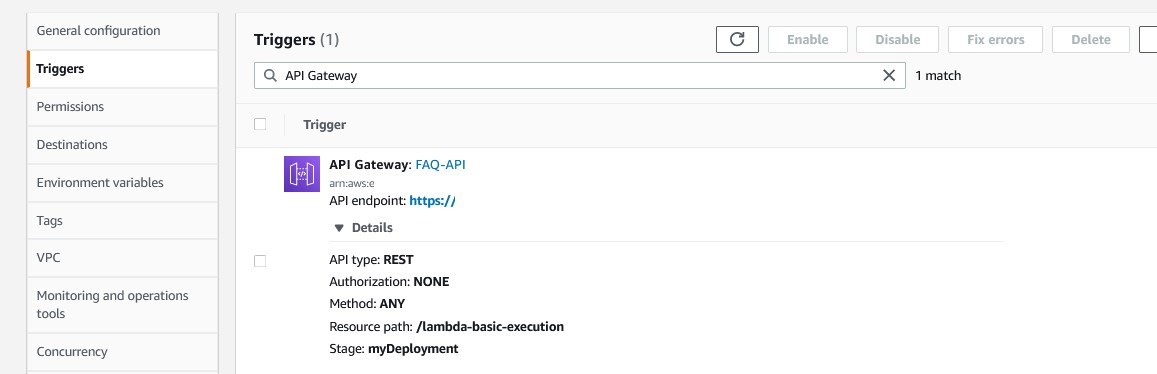
A new browser tab will open. You should see a random FAQ entry, such as:

The Lambda function can also be tested in isolation.
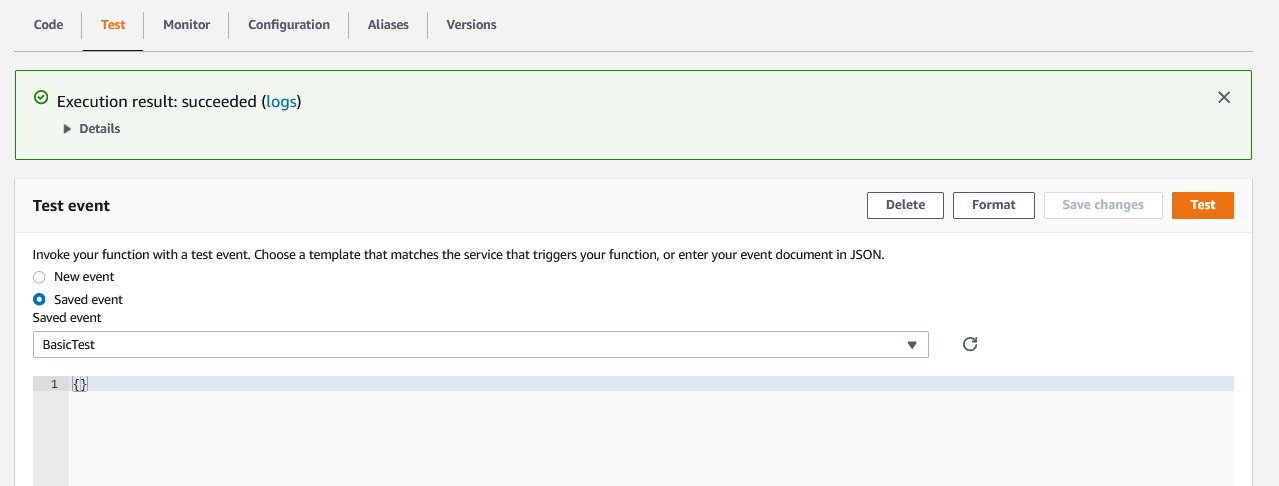
The output shows the FAQ entry wrapped inside a body parameter.
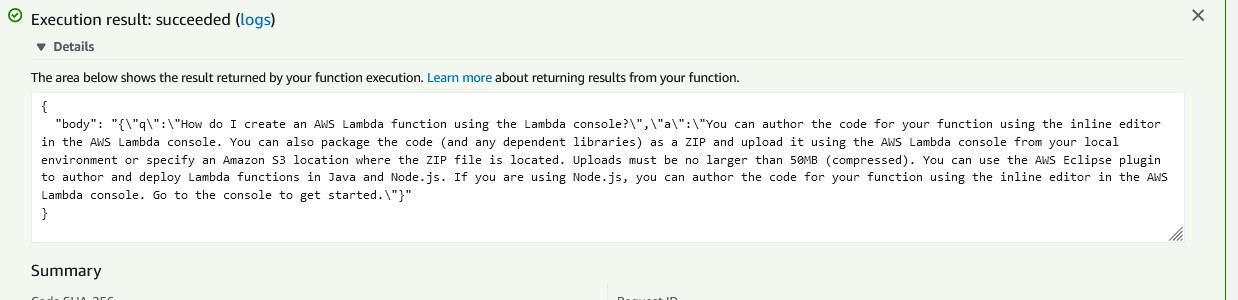
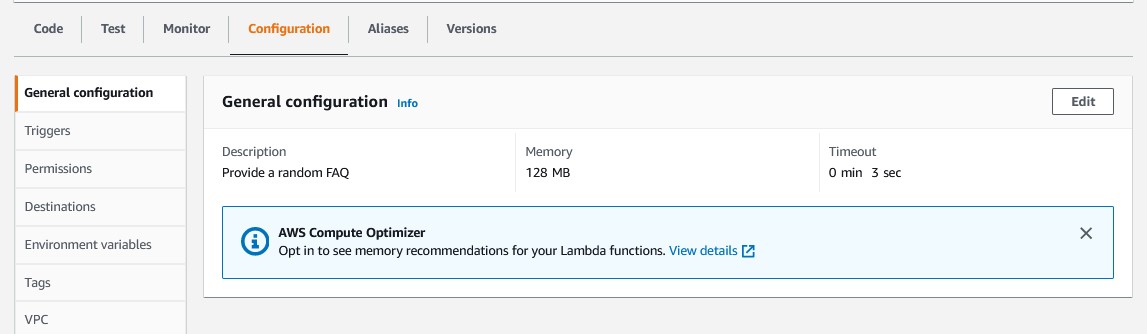
Below Execution result are two columns. The Summary displays the total execution time for the Lambda function and the resources consumed. The Log output displays logging information. In this section, you will see any console logging as well as any error messages.
Click the Monitor tab. Click View logs in CloudWatch
Click on one the log streams.
You will be presented the same event data that was displayed in the Lambda Management Console. Examine the contents of each line to view the log information.
What’s next?
Here are some additional things you could do to extend the functionality of your microservice:
Remember to delete:
References:
(http://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/welcome.html)
(http://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/welcome.html)
(https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/how-to-create-api.html)
(https://www.ics.uci.edu/~fielding/pubs/dissertation/rest_arch_style.htm)
